Introduction
Google Bard vs Anthropic AI vs ChatGPT – this comprehensive guide provides an in-depth comparative analysis of these leading advanced AI models. We extensively evaluate Bard vs Anthropic vs ChatGPT to reveal their key differences in architecture, training techniques, capabilities, limitations, and ideal real-world applications.
These sophisticated language models utilize complex neural networks and vast datasets to generate remarkably human-like text. But how exactly do their systems work and what are they best suited for? Our insightful guide cuts through the hype to uncover what makes each AI giant distinct. If you want to truly understand Google Bard, Anthropic AI, and ChatGPT beyond the buzz, this is an essential comparative evaluation.
Overview of Google Bard, Anthropic AI, and ChatGPT
1. What is Google Bard?

Unveiled in 2022, Google Bard aims to be an AI assistant that can understand the context and generate informed responses. It uses transformer-based neural networks trained with reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
Key features:
- Language model designed for search, conversation, and content creation
- Leverages BERT, transformers, RLHF
- Aims to avoid false information and biased responses
- Integrated into Google products like Search, Maps, Docs
2. What is Anthropic AI?

Founded in 2021, Anthropic focuses on developing safe and beneficial AI systems aligned with human values. Their models emphasize interpretability, allowing users to understand how they reach conclusions.
Key features:
- Uses Constitutional AI approach with transparency and oversight
- Improves on existing methods like reinforcement learning
- Designed to be predictable, interpretable, and controllable
- Avoid harm through safety techniques like self-supervision
3. What is ChatGPT?

Created by OpenAI and launched in 2022, ChatGPT is an AI chatbot that generates human-like conversational text using transformer models. It is trained with both supervised learning and RLHF.
Key features:
- Advanced natural language processing for dialogues
- Utilizes GPT-3 model architecture
- Trained on massive text datasets and conversations
- Improved responsiveness through fine-tuning
Comparing the AI Models

1. Training and Architecture
- Google Bard uses BERT and transformer models plus RLHF training. This allows bidirectional context understanding.
- Anthropic AI builds on existing transformer AI but adds techniques like constitutional AI for interpretability.
- ChatGPT leverages GPT-3, a transformer network trained on internet data using RLHF.
2. Strengths and Capabilities
- Google Bard: Excellent at search, summarization, and multitasking across Google products. Responsive and conversational.
- Anthropic AI: Focuses on transparency, predictable behavior, and avoidance of harmful instructions. Interpretable.
- ChatGPT: Impressive natural language processing and ability for dialogues. Human-like and customizable responses.
3. Limitations and Weaknesses
- Google Bard: Can sometimes respond inaccurately or inappropriately. Limited real-world knowledge.
- Anthropic AI: Still in the research stages, so capabilities are constrained. High resource requirements.
- ChatGPT: Prone to hallucination, bias, and improper responses. Lacks deeper reasoning.
4. Ideal Use Cases
- Google Bard: Integrated into Google’s products and services to assist users. Also creative writing and conversational search.
- Anthropic AI: Research, controlled testing environments, and applications where transparency is critical.
- ChatGPT: Conversational agents, entertainment purposes, basic assistance for content writing.
Diving Deeper into Each AI System
1. The Making of Google Bard
Google Bard represents an evolution in AI assistants by Google Research. Let’s analyze its key capabilities:

- Conversational Ability: Google Bard can engage in intelligent dialogue by understanding context and responding relevantly. This is enabled by transformer neural networks and RLHF training.
- Multitasking Skills: Bard can summarize lengthy articles, translate languages, compose emails and documents, and more. Its versatile performance is powered by BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
- Creative Writing: Bard can craft poems, continue stories, and generate creative content thanks to its aptitude for natural language processing. This showcases its prowess at text generation.
- Integration with Google: Being embedded into Google products allows Bard to assist users directly. For instance, it can suggest email drafts in Gmail or point out errors in Docs.
- Harm Avoidance: Google applies techniques like bounded rationality and cross-referencing information to ensure Bard avoids providing dangerous, unethical, or false guidance.
However, Bard has limitations including potential bias in training data, gaps in world knowledge, and failures in reasoning for complex judgment. Overall though, its conversational nature and integration across Google position it as a frontrunner in AI assistance.
2. Inside Anthropic AI
Anthropic Claude AI takes a safety-focused approach to developing AI aligned with human values. Here are some of its key attributes:

- Constitutional AI: Anthropic’s AI architecture incorporates transparency, oversight, and compliance like a legal constitution. This technique formalizes human oversight over AI systems.
- Interpretability: A core focus is making AI behavior interpretable, allowing users to understand the rationale behind its actions by explaining its reasoning process.
- Improved Learning: Anthropic AI utilizes self-supervised learning to enable models to learn safely from limited data while avoiding the reinforcement of unwanted biases that exist in large internet datasets.
- Control Mechanisms: Human constitutional oversight coupled with engineering techniques to make models predictable and controllable reduces risks associated with advanced AI.
- Research Orientation: As an organization focused on research, Anthropic dedicates resources to rigorous testing and responsible development practices to make AI safer and more reliable over the long term.
However, drawbacks include its intensive computing requirements and its early stage of development. But Anthropic’s interpretability and safety-oriented approach sets it apart from other AI models.
3. Demystifying ChatGPT
As a dialogue agent created by OpenAI, ChatGPT possesses some standout qualities:

- Human-like Language: ChatGPT exhibits remarkable ability for natural language conversations. Its responses are articulate, nuanced, and contextually relevant.
- Knowledgeable: Training on vast texts spanning different topics imparts ChatGPT with broad general knowledge for intelligent discussions on a wide range of subjects.
- Creative Capabilities: ChatGPT can generate original poems, fiction stories, musical lyrics and more showcasing its creative potential.
- Usefulness: It serves numerous useful purposes like answering questions, translating text, summarizing concepts, resolving coding issues and providing tutoring across academic subjects.
- Configurability: Users can fine-tune ChatGPT by providing tailored instructions and feedback to shape its behavior as per their requirements.
However, some drawbacks include the high chance of incorrect or nonsensical responses, unintended harmful guidance, and reinforcement of societal biases. But its advanced language skills make ChatGPT a versatile AI model for a breadth of applications.
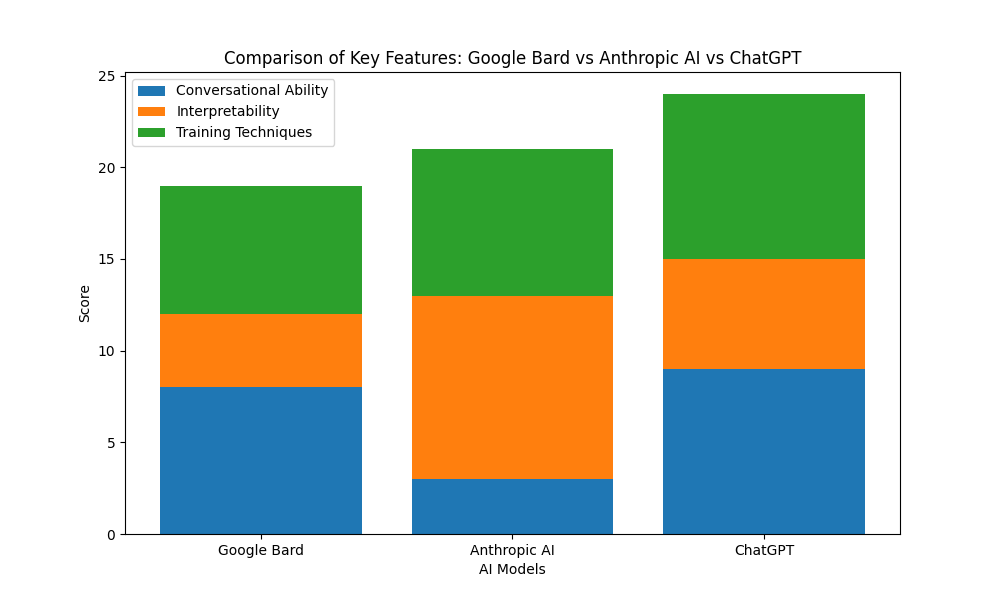
Google Bard vs Anthropic AI vs ChatGPT: Key Differences

| Main Points | Google Bard | Anthropic AI | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Technology | BERT, Transformers | Constitutional AI, Interpretability | GPT-3, Transformers |
| Primary Goal | Conversational search and content creation | Transparent and aligned AI | Human-like conversational agent |
| Strengths | Multitasking across Google products, responsiveness | Predictability, interpretability, safety | Creative expression, broad knowledge, usefulness |
| Limitations | Inaccuracy, gaps in reasoning | Early research stage, high compute needs | Hallucination, bias, harmful guidance |
| Best Suited For | Google integration, search, writing | Research, critical applications needing transparency | Conversational agents, entertainment |
This comparison summarizes how the underlying technology, objectives, strengths, weaknesses and ideal use cases differ between Google Bard, Anthropic AI, and ChatGPT.
Key Takeaways
- Google Bard, Anthropic AI, and ChatGPT represent significant innovations in AI, utilizing complex neural networks and vast training datasets.
- Google Bard excels at search, summarization, and integration across Google’s products. Anthropic AI focuses on interpretability and safety. ChatGPT mimics human dialogues remarkably well.
- Each AI system has unique strengths but also inherent weaknesses and limitations that constrain its capabilities in different ways.
- Matching these AI models to suitable use cases is crucial – Google Bard for Google products and services, Anthropic for research and transparency needs, and ChatGPT for conversational agents.
- While narrow AI models have come far, achieving general human intelligence requires further advances in multi-tasking, reasoning, and real-world knowledge.

The Future of Advanced AI
1. Where is AI innovation heading?
Current state-of-the-art AI like Bard, Anthropic, and ChatGPT still represent narrow AI, needing human oversight and having significant limitations. While their capabilities are impressive, the goal of developing strong or general AI with the versatility and reasoning power of humans remains challenging.
Ongoing innovation in AI research focuses on key frontiers like:
- Multitask versatility: Ability to apply knowledge and skills flexibly across diverse tasks.
- Memory networks: Storage and lookup of relational knowledge representations to leverage contextual information.
- Causal reasoning: Understanding causality allows counterfactual inferences central to creativity and planning.
- Hybrid models: Combining neural networks, symbolic systems, knowledge graphs, and other techniques to overcome the limitations of single approaches.
- Self-supervised learning: Enables models to learn effectively from unlabeled data in a more scalable and generalizable manner.
- Robustness: AI that behaves reliably under wide variations in inputs and environments outside its training domain.
- Auditing and oversight: Techniques to monitor model behavior, detect issues, and correct errors proactively.
Advancements across these frontiers will pave the path ahead for more capable, trustworthy, and beneficial AI systems.

2. When will AI achieve human-level intelligence?
Predicting exactly when AI will reach human intelligence remains speculative, but researchers estimate possible timelines:
- Conservative estimates range from decades to hundreds of years due to the extreme difficulty of emulating the breadth of human cognition.
- Median forecasts center around 20 to 70 years as AI capabilities continue accelerating, perhaps achieving human parity in targeted domains first.
- Optimistic predictions envision human-level AI emerging within the next decade or two based on the exponential pace of progress in deep learning.
However, transformational advances are needed in fundamental areas like reasoning, knowledge representation, abstraction, planning, and creativity to attain the flexibility and general intelligence central to human cognition. Multi-disciplinary collaboration combining neuroscience, cognitive science, computer science, and philosophy will likely accelerate this quest for artificial general intelligence.
3. What are the implications of more advanced AI?
As AI becomes more capable and autonomous in the coming years and decades, it can usher in both profound opportunities and risks for individuals, institutions, and societies:
| AI Capability | Benefit | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Automating tasks | Increased efficiency, productivity | Unemployment from job displacement |
| Personalized recommendations | Improved user experience, satisfaction | Infringement on privacy from extensive data collection |
| Predictive analytics | Optimized resource allocation, risk detection | Perpetuating biases from flawed or unrepresentative training data |
| Natural language processing | More intuitive human-computer interaction | Misuse by malicious actors to generate disinformation |
| Computer vision | Automated visual inspection, enhanced safety | Vulnerabilities to adversarial attacks or misclassifications |
| Autonomous systems | Faster response times, access to hazardous environments | Lack of human oversight or control |
Realizing the potential upsides while mitigating the dangers will require ethical AI development aligned with human values, robust governance frameworks, and democratization of the gains from increasingly intelligent systems.
This proactive, wise management of progress in AI constitutes one of the key challenges and responsibilities facing researchers, corporations, governments and society overall as these transformative technologies continue advancing.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How was Google Bard developed?
Google Bard was created by Google Research using transformer neural networks and reinforcement learning from human feedback. It builds on foundational models like BERT to understand context, while also being trained directly through dialogues.
2. What is Anthropic AI’s Constitutional AI?
Constitutional AI is Anthropic’s approach to architecting AI systems with layers of transparency, oversight, and compliance built-in, like constitutions for democratic societies. This technique aims to make AI more controllable.
3. What are the main risks of language models like ChatGPT?
Key risks with ChatGPT and similar AI include inaccuracy, bias, failure to generalize, potential to encourage harmful behavior, and malicious use cases like generating misinformation.
4. How is GPT-3 different from BERT?
GPT-3 is a generative transformer model trained to predict text, while BERT is a bidirectional model focused on understanding language. GPT-3 powers text generation in ChatGPT, whereas BERT enables search improvements in Google Bard.
5. What are the biggest challenges in developing human-level AI?
Major obstacles to achieving human-level AI include limitations in multitasking, memory, knowledge representation, reasoning, abstraction, common sense, planning, creativity, and generalizability beyond the training domain.
6. Is there a risk of AI becoming too dangerous?
Potential dangers from highly advanced AI include loss of control, misaligned objectives, stifling of human autonomy, and catastrophes from uncontrolled optimization unchecked by ethics and human values. Researchers are working to mitigate these risks.
7. When will AI be smarter than humans?
There is no consensus, but expert predictions range from decades to hundreds of years due to the extreme difficulty of emulating the breadth and generality of human cognition. Critical breakthroughs in reasoning, knowledge, and learning are needed.
8. How does AI interpret and respond to language input?
AI systems like Bard, Anthropic, and ChatGPT process language using transformer neural networks that analyze the context across thousands of words to extract meaning and generate relevant text responses word-by-word.
9. Why is more training data important for AI?
More high-quality and diverse training data helps AI models better generalize across different contexts and tasks. Data limitations today result in deficiencies like bias, failure to transfer learning, and lack of robustness.
Conclusion
The emergence of advanced AI like Google Bard, Anthropic AI, and ChatGPT foreshadows a future powered by increasingly intelligent systems. But realizing both their transformative potential and risks calls for nuanced evaluation of their capabilities, diligent oversight of their impacts, and steadfast guidance by human values as they continue evolving.
Comparatively analyzing these models today crystallizes their progress and shortcomings, while illuminating promising research directions. Creating wise, multi-disciplinary governance and democratizing the gains will be pivotal to ensuring these technologies make the world more just, equitable, and empowering for all.
Understanding the origins and inner workings of AI also connects us to the remarkable ingenuity underpinning their development. Appreciating both the technology and its burgeoning responsibility will be essential as artificial intelligence progresses from narrowly focused tools to eventually, perhaps, digital minds that think alongside our own.

2 thoughts on “Google Bard vs Anthropic AI vs ChatGPT: The Shocking Truth about the Big 3 AI Giants”